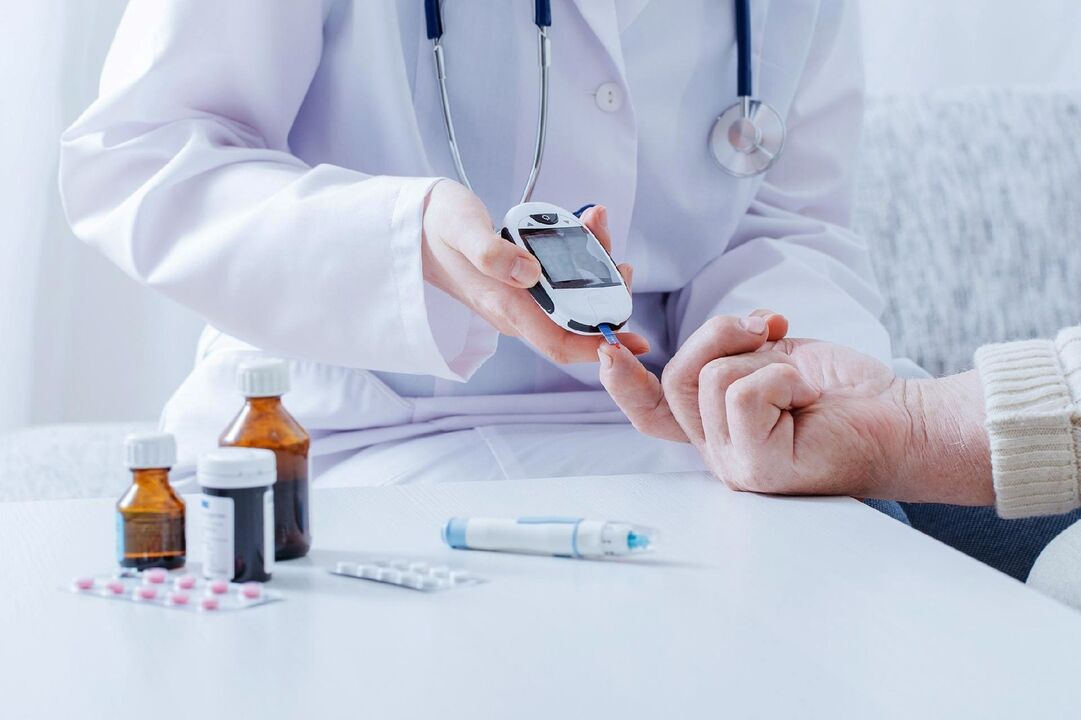
What is diabetes?
How do I know if I have diabetes?
- Increased urine output occurs due to an increase in urinary pressure due to the glucose dissolved in it (normally there is no glucose in urine). Symptoms include frequent and heavy urination, including at night.
- Persistent unquenchable thirst is caused by massive water loss in the urine and increased blood osmolality.
- Constant insatiable hunger. This symptom is caused by the metabolic disorder of diabetes, which is the inability of cells to absorb and process glucose in the absence of insulin (starvation in abundance).
- Weight loss, especially a classic symptom of type 1 diabetes, is a common symptom of diabetes that occurs despite an increased appetite.
So if you notice these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately!
What are the types of diabetes?
Are there at-risk groups?
What complications can diabetes cause?
- Eyes - The retina is affected, and diabetes can lead to cataracts (clouding of the lens) and blindness (changes in the retina).
- Teeth - All diseases in the mouth accelerate due to lack of blood supply. Diabetes is often diagnosed in the dental office with patients complaining of swollen gums and loose teeth.
- Heart - Affected by diabetes; changes in the heart muscle due to high cholesterol, changes in blood vessels, leading to coronary heart disease.
- Liver - When diabetes is poorly compensated, its normal functions are disrupted and the liver becomes enlarged.
- Diabetes directly affects the kidneys, leading to diabetic nephropathy.
- reproductive system. Diabetes can cause impotence in men; in women it can lead to miscarriage, premature birth and intrauterine death.
- For women with diabetes, the process of pregnancy and childbirth is complex. Pregnant women with diabetes require mandatory supervision by two specialists (endocrinologist and obstetrician).
- Legs and Feet – Diabetes develops due to damage to blood vessels and nerves. Possible results are trophic ulcers, gangrene, and loss of limbs. In addition, feet and nails are also susceptible to fungal infections.
- Joints are more susceptible to processes such as salt deposition than healthy people; in addition, people with diabetes may also experience changes in their joints.
- The circulatory system is directly affected by diabetes, which leads to all the above-mentioned diseases. People with diabetes often have high blood pressure. Note that another factor that stimulates vascular damage in diabetes is smoking.
Can we cure diabetes?
Should diabetes be treated?
Are blood sugar levels difficult to control?
Prevent diabetes
- Active lifestyle and weight control. Diabetes is directly related to obesity. Physical activity helps lower blood sugar and reduces the need for insulin.
- Proper nutrition. Eating foods rich in dietary fiber can normalize intestinal function and lower cholesterol levels. These products include all fruits and vegetables, legumes, dairy products, nuts, and more.
- Avoid excessive consumption of flour, sweets, pasta and baked goods. Eat only bread made from whole grains.
- Avoid stress and don't smoke. One of the causes of diabetes is stress and anxiety. Stress and smoking reduce the body's resistance to diabetes.
- If you are over 40, monitor your blood sugar levels regularly. A sugar test is also necessary for those prone to obesity and living a sedentary lifestyle.